
- #Calculate residual how to
- #Calculate residual verification
- #Calculate residual iso
- #Calculate residual zip
Now organizations are expected to significantly reduce residual risks throughout their supply chain to limit the impact of third-party breaches by nation-state threat actors.

#Calculate residual iso
To be compliant with ISO 27001, organizations must complete a residual security check in addition to inherent security processes, before sharing data with any vendors.īut in 2021, residual risk has attained an even higher degree of importance since President Biden signed the Cybersecurity Executive Order. This is a popular information security standard within the ISO/IEC 2700 family of best security practices that helps organizations quantify the safety of assets before and after sharing them with vendors. Residual risk is important because its mitigation is a mandatory requirement of ISO 27001 regulations. Why is Residual Risk so Important in 2023?
#Calculate residual how to
To learn how to identify and control the residual risks across your digital surfaces, read on. Generation from facilities that cannot be readily assigned to eGRID subregions is excluded from these residual mix emissions rates.Residual risk is the threat or vulnerability that remains after all risk treatment and remediation efforts have been implemented.Įven with an astute vulnerability sanitation program, there will always be vestiges of risks that remain, these are residual risks.īecause they will always be present, the process of managing residual risk involves setting an acceptable threshold and then implementing programs and solutions to mitigate all risks below that threshold.
#Calculate residual zip
The total CO 2 emissions for each region are then divided by this new generation number for each subregion, resulting in an adjusted emissions rate (lb CO 2/MWh) that accounts for use of renewable energy from a Green-e® Energy certified product.įor this calculation, each U.S.-generated MWh is assigned to a specific eGRID subregion, with generating facilities assigned to eGRID subregions using facility zip codes and Energy Information Agency data. The residual mix emissions rate is calculated by first subtracting all unique Green-e® Energy certified sales (in megawatt-hours ) from the total generation within each subregion.
#Calculate residual verification
These rates are calculated using the data collected by Green-e® Energy during annual verification of certified sales and the most recent emissions and generation data provided by eGRID in the U.S. Residual Mix Rate Calculation Methodology Green-e® Energy also offers the Green-e® Energy Summary of WRI Scope 2 Guidance, a guide for purchasers of Green-e® Energy certified renewable energy on how to calculate Scope 2 emissions. Use of these numbers is compatible with WRI’s Greenhouse Gas Protocol Scope 2 Guidance, which defines residual mix in more detail. Users reporting their GHG data should cite the use of these residual mix rates in their accounting. Until such time, Green-e® residual mixes are available, which factor out all Green-e® certified sales of renewable energy. Regional residual mix emissions rates that factor out all specified electricity purchases are not yet available for all regions of the U.S. When calculating the emissions from unspecified purchased or acquired electricity (considered “Scope 2” emissions, as defined by the World Resources Institute ), where more-accurate information about the resources and emissions associated with electricity use is not available from the user’s state, region, or electricity supplier, residual mix emissions rates should be used. Individuals can figure out which eGRID subregion in which they are located by using the EPA’s Power Profiler tool. The residual mix emissions rate used should be based on the eGRID subregion in which the electricity is consumed. It does not include any data that is not reported to Green-e.
generation and emissions rate at the time of publication. Green-e® residual mix emissions rates are published every Spring using Green-e® voluntary renewable energy market sales data collected during the annual Green-e® verification audit from two calendar years prior and the most recent U.S.
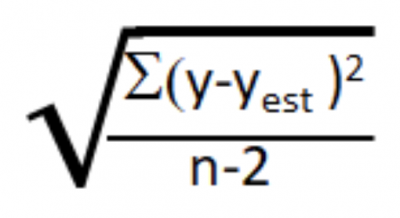
The table provides the “Green-e® residual mix emissions rate,” an emissions rate that is adjusted to remove all Green-e® Energy certified sales for each Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID) subregion (see eGrid subregion map). The information in these tables can be used to calculate the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with untracked and unclaimed U.S.-based sources of electricity, based on location of consumption.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
